A standpipe is a ground-supported storage tank with a height that is greater than its diameter. Its design helps generate storage and pressure with a low upfront cost compared to elevated tank geometries. While there are cost advantages to standpipes, its geometry is a liability: tall and skinny tanks naturally promote thermal stratification and harm water quality. Standpipes have a higher surface area to volume ratio – meaning that more surface area is exposed to heat from the sun, and there’s less volume inside the tank to absorb that heat. Additionally, the limited cross-sectional area of a standpipe makes it difficult to exchange heat between the hot water at the top of the tank and cold water at the bottom, resulting in thermal stratification. Below we have compiled four signs that indicate your standpipe is thermally stratified.
Read More
Topics:
active mixing,
eliminate stratification,
drinking water quality,
PAX Water Mixer,
storage tanks,
water circulation,
passive mixing,
mixing systems,
low turnover
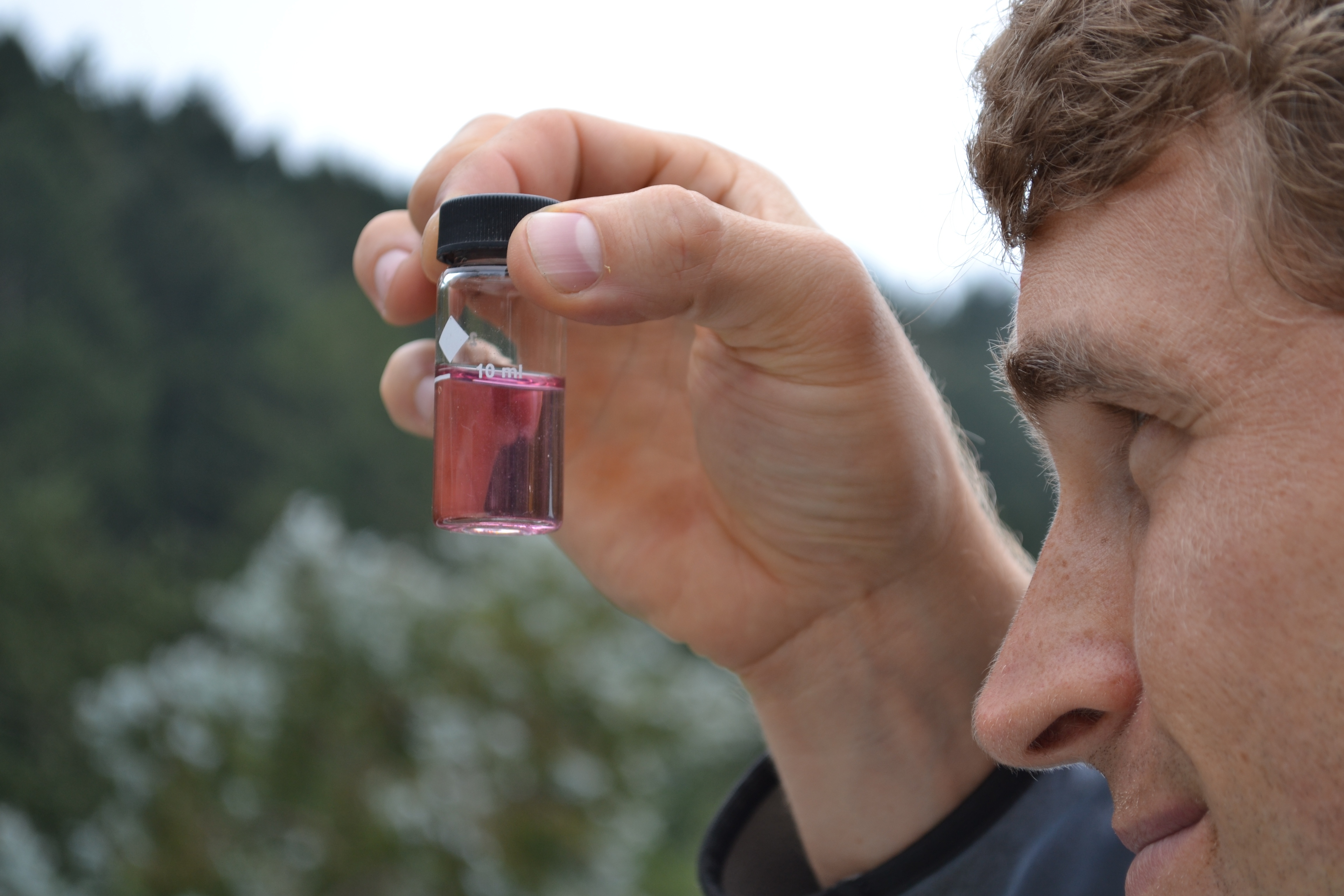
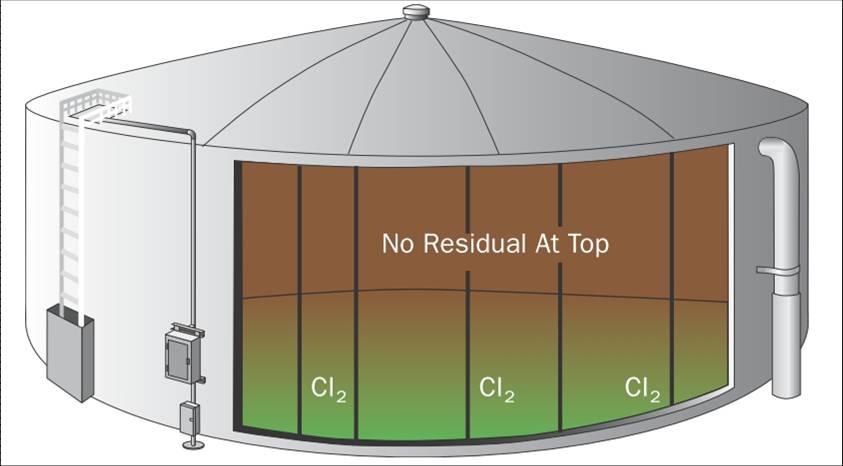
When summer temperatures rise, chlorine demand inside storage tanks increases and water quality can degrade. Warm water temperatures, particularly at the top of the tank, increase biological growth, deplete residual disinfectant and increase the formation rate of disinfection by-products (DBPs). Thermal stratification also creates hot and humid conditions inside the headspace, greatly accelerating corrosion rates inside steel tanks. One effective solution to combat stratification and maintain disinfectant residual levels is active mixing. A powerful mixer eliminates thermal and chemical stratification inside tanks and reduces the growth of biofilms and DBPs. Below, we answered three common questions on maintaining residual disinfectant levels inside water storage tanks.
Read More
Topics:
active mixing,
eliminate stratification,
drinking water quality,
PAX Water Mixer,
storage tanks,
water circulation,
passive mixing,
mixing systems,
low turnover
Charles Fishman (author of The Big Thirst) wrote a piece for the Washington Post last month on “Five Myths About Water.” Number two on Charles’ myth list is “bottled water is better than tap water,” where he unveils that tap water is actually MORE closely monitored than bottled water and that in blind taste tests “people can’t reliably pick bottled from tap.” At PAX Water, Charles’ article got us thinking about some of the myths we’re trying to bust in the drinking water industry. Here are our top five:
Read More
Topics:
active mixing,
eliminate stratification,
drinking water quality,
PAX Water Mixer,
storage tanks,
water circulation,
passive mixing,
mixing systems,
low turnover
The AWWA held a webinar on October 6, 2010 entitled Sustainable Water Quality Management within the Storage Tank: Part 2 (you can listen to a rebroadcast here).
Read More
Topics:
active mixing,
storage tanks,
WaterMix,
biofilms,
mixing systems
We learned this week that an engineer (who shall remain unnamed) presented a paper at the DSS meeting in Maryland about water age modeling in which he claimed that mixing CANNOT decrease water age.
Read More
Topics:
active mixing,
disinfectant residual,
storage tanks,
high water age,
mixing systems
The EPA recently announced a new strategy to provide clean, safe drinking water and a novel means by which those of us in the water industry, and citizens in general, can comment on it: an on-line discussion forum.
Read More
Topics:
Water Quality,
storage tanks,
mixing systems,
dbp formation
Are you going to ACE10 next week in Chicago? PAX Water Technologies will be there.
Read More
Topics:
eliminate stratification,
mixing systems
Because mixing in water storage tanks is a new concept, many people don’t realize that there are actually two different types of mixing: active mixing and passive mixing. Most state regulators don’t appreciate the difference either.
Read More
Topics:
Water Quality,
eliminate stratification,
PAX Water Mixer,
storage tanks,
impeller,
mixing systems
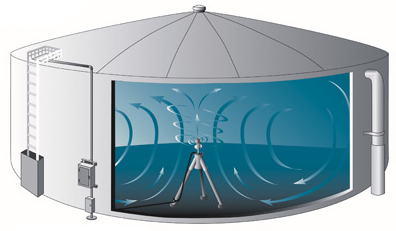
Active mixing has been shown to eliminate thermal stratification, prevent the formation of dead zones, reduce disinfectant residual loss and improve overall water quality in potable water storage tanks.
Read More
Topics:
eliminate stratification,
water circulation,
high water age,
mixing systems